A low prime rate helps companies cheaply borrow money so they can expand and create jobs and low mortgage rates help people afford more expensive homes. The Fed paid interest to banks because.
Why Or Why Not Keep Paying Interest On Excess Reserves Liberty Street Economics
It is interest on credit available to the Fed.

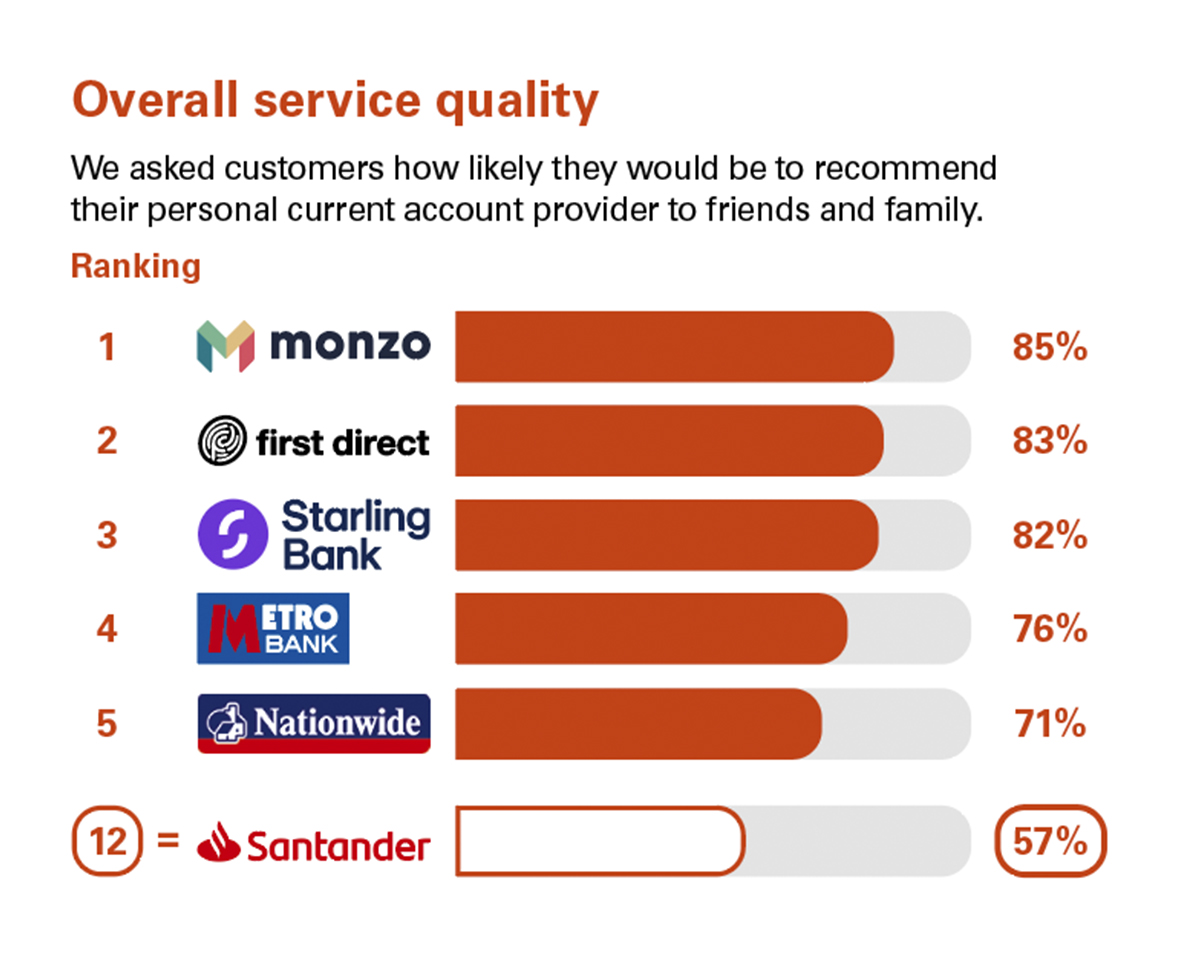
Why does the fed pay interest to banks. So the balances of Excess Reserves have plunged and the interest rate the Fed pays on those reserve balances has jumped. Both factors combined caused the Fed to pay a record 385 billion to US banks and foreign banks in the US. The Fed wanted QE to revive the.
Why does the Fed pay interest to banks. Why does The Fed raise or lower interest rates. Maybe the Federal Reserve proposes paying interest to banks because banks are strapped for capital.
The Feds ability to pay interest on reserves has become essential. Although the payment of interest on reserves provides no meaningful subsidy the Fed does face an appearance problem from the fact that it is writing checks to banks. A bank borrows money from the governments central bank utilizing what is known as the discount.
Listen to this article Four decades ago Milton Friedman recommended that central banks like the Federal Reserve pay interest to depository institutions on the reserves they are required to hold against their deposit liabilities. It is interest on loans taken by the Fed. Just as you sometimes need loans to meet your business or personal financial goals so do banks.
This problem will likely get. It is interest on government investments. Once the Fed began paying IOR at a rate slightly higher than T-bill yields however it became much.
O2z1qpv and 10 more users found this answer helpful. Borrowing from the Fed allows banks to get themselves back over the minimum reserve threshold. This proposal was intended to improve monetary policy by making it easier to hit short-term interest rate targets.
Thus banks got rid of excess reserves beyond their legally required reserves as quickly as possible like a hot potato. That means we the taxpayers are paying 36 billion annually to private banks for the privilege of parking their excess reserves at one of the most secure banks in the world parking their reserves rather than lending them out. The Fed influences the economy by raising and lowering its target for the federal funds rate.
Before the Fed could pay interest on reserves it provided a supply of reserves that was close to the total level of banks demand. The Fed rebates its profits to the government after deducting its costs and interest paid to banks is one of those costs. Thats because banks could earn a positive interest rate on safe assets such as T-bills but the Fed paid no interest at all on bank reserves.
The Fed rebates its profits to the government after deducting its costs and interest paid to banks is one of those costs. The Fed recently acted emergently to pump 25 billion into Bear Stearns and an additional 30. The Feds primary purpose throughout QE was to lower interest rates and spur economic growth.
At its December meeting the Fed raised this rate to 24. This scarcity of reserves was important to achieving the target for the level of the FOMCs policy rate the federal funds rate. Which statement best describes how the Feds use of open market operations affects banks.
It is interest on money held in reserve. It is interest on money held in reserve. One of the ways the Fed carries out its long list of duties is by controlling the recommended target fed funds rate which is the interest rate charged by one bank lending money to another bank.
Banks base all short-term interest rates on the fed funds rate. That means we the taxpayers are paying 36 billion annually to private.